In today’s constantly shifting global trade environment, organizations face an unprecedented mix of regulatory pressure, operational complexity, and geopolitical uncertainty. Compliance is no longer just a defensive function—it is a strategic capability. And according to the 2024 Descartes Trade Compliance Benchmark Survey, technology is becoming the defining factor that separates companies that struggle from those that grow.
Key Takeaways
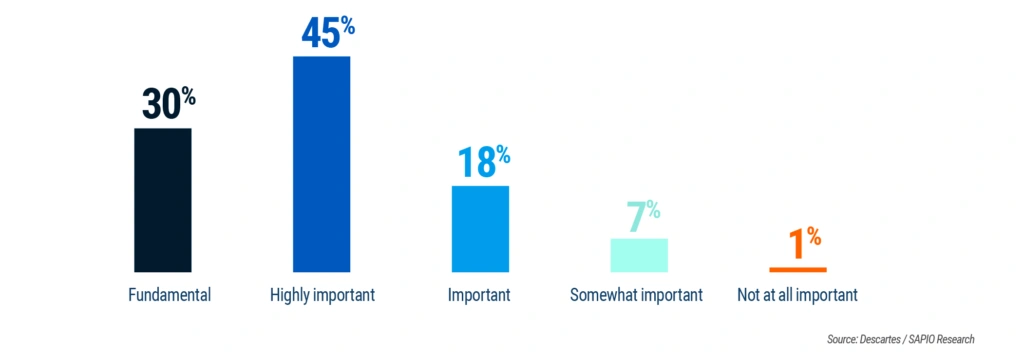
- Technology drives growth: 75% say trade compliance technology is fundamental or highly important—and 86% of high-growth companies agree.
- Manual processes create risk: Automated screening, export licensing, and classification reduce errors and accelerate onboarding.
- Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) and forced labor rules demand deeper visibility: Supply chain mapping and data intelligence are now essential.
- Mid-sized companies are highly vulnerable: Compliance technology helps bridge resource gaps and strengthen compliance resilience.
- Compliance is a competitive differentiator: Organizations increasingly view trade compliance as an asset, not just an obligation.
With more than 800 global trade and compliance leaders surveyed, the findings are clear: organizations that prioritize technology not only improve compliance outcomes—they unlock new efficiencies, reduce risk, and accelerate growth. For compliance teams navigating mounting regulatory demands and supply chain volatility, compliance technology has become an essential infrastructure.
Compliance Technology: A Proven Growth Enabler
The survey reveals an unmistakable trend: technology investment directly correlates with organizational growth. Three-quarters (75%) of respondents say technology is fundamental or highly important to their growth strategy, and that number climbs to 86% among companies expecting more than 15% growth in the next two years.
This reinforces what many compliance and supply chain professionals already see firsthand—manual, spreadsheet-driven processes can no longer keep pace with regulatory change. Automated export classification tools, denied party screening, and integrated trade data accelerate decision-making and help teams shift from administrative work to strategic opportunity.
Figure 1. How Organizations Perceive Technology as a Driver of Growth
Growth-oriented companies are also more likely to make technology a primary lever for overcoming compliance challenges. In fact, 38% of all organizations—and 47% of high-growth companies—cite technology as their top strategy to ensure continued growth.
Managing Complexity: Trade Barriers, ESG, and Geopolitical Pressure
The global compliance landscape continues to expand and evolve. According to the survey, the top challenges facing organizations include:
- Tariffs and trade barriers (50%)
- ESG compliance requirements (43%)
- Geopolitical instability (42%)
- Supply chain disruptions (42%)
These pressures are not only increasing in frequency but also in the depth of due diligence required. For example, regulations such as the Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) require extensive supply chain mapping and traceability beyond immediate Tier-1 suppliers—an enormous task for organizations relying solely on manual processes.
Trade compliance technology allows organizations to maintain the visibility and responsiveness required to remain compliant in this environment. Automated workflows, integrated data, and real-time screening reduce the risk of errors, delays, and costly enforcement actions.

Embedding Trade Compliance in Core Business Processes
One of the most significant shifts highlighted in the survey is the growing need to embed trade compliance directly into enterprise systems. Organizations recognize that manual reviews, outdated data, or disconnected systems create unnecessary risk.
The survey research paper emphasizes the heavy resource burden of manual denied party screening and export license management, noting that automation reduces errors, accelerates licensing processes, and enforces consistent controls across operations.
Embedding automation enables companies to identify compliance issues earlier, move opportunities through the pipeline faster, and reduce friction during customer and supplier onboarding. This is especially critical now that regulators can sanction entities using the same address as restricted parties—a level of nuance only technology-driven screening can reliably detect.
Compliance Technology Innovation: Artificial Intelligence (AI) Takes Center Stage
As automation evolves, AI is rapidly becoming a core tool in international trade compliance. The survey shows strong adoption, with 70% of companies describing themselves as early adopters or fast followers of new technology.
AI’s impact is particularly strong in classification, where it can:
- Analyze product attributes
- Match dataset inputs against classification requirements
- Identify license requirements
- Reduce processing time compared to manual review
For compliance teams that spend countless hours reviewing classifications or verifying data, automation unlocks substantial efficiency, accuracy, and consistency.
Figure 2. Trade Compliance Technology Capabilities for Growth

Mid-Sized Organizations: High Exposure, High Need
A striking insight from the survey is the vulnerability of mid-sized companies. Organizations with 501–1,000 employees are significantly more likely to describe themselves as early technology adopters because they face the same compliance demands as large enterprises—without the same resources or external support.
Mid-sized companies are also more likely to expect continued supply chain disruptions and receive less proactive guidance from legal counsel, brokers, and logistics partners. Technology becomes a force multiplier—enabling them to enhance visibility, embed consistent compliance, and avoid staffing strain.

Supply Chain Mapping Becomes Essential
As global regulations expand deeper into forced labor prevention, environmental stewardship, and ethical sourcing, supply chain mapping has moved from an enhancement to a necessity.
The paper notes that while many organizations can map direct suppliers, visibility decreases rapidly beyond tier 2 or 3, especially for mid-sized companies. The depth of information now required—including product components, raw material origin, and even packaging sources—cannot be achieved manually at scale. Technology providers and automated platforms are becoming essential partners in meeting supply chain due diligence expectations.
Trade Compliance as Competitive Advantage
A growing number of organizations view compliance as more than a risk-management function. Nearly one-third (32%) now consider it a competitive asset, and another 32% see it as a customer service differentiator.
This shift is driven by the realities of global trade. Companies that can rapidly onboard partners, confirm due diligence, access trusted data, and respond agilely to disruptions outperform those reliant on manual processes.
Technology also aligns directly with the top priorities cited by organizations, including global trade compliance (56%), cybersecurity (41%), and ESG compliance (37%).
Figure 3. Top Priorities for Trade Compliance Technology

To stay competitive, companies are focusing on global trade intelligence, advanced analytics, and automated export controls—capabilities that streamline operations and reduce risk simultaneously.
Conclusion: Technology Is Now the Backbone of Trade Compliance
The findings of the 2024 Descartes Trade Compliance Benchmark Survey underscore a simple but powerful truth: compliance technology is no longer optional in global trade. It is a prerequisite for efficiency, agility, and growth.
As regulations tighten, supply chains evolve, and geopolitical risk continues to rise, organizations that embed automation, real-time data, integrated denied party screening, and AI-driven classification will be best positioned to navigate change—and capitalize on new opportunities.
Figure 4. Leaders’ Approach: Investing in Compliance Technology for Trade Challenges

How Descartes Trade Compliance Technology Supports Global Growth
By partnering with Descartes, organizations can access timely, accurate global trade content, streamline compliance processes, and strengthen supply chain resilience.
With the comprehensive suite of Trade Intelligence Solutions from Descartes, companies can turn complexity into opportunity and ensure compliance confidence across every border.
Learn more about how Descartes Trade Compliance Solutions can help your business stay compliant and competitive.
See also related research studies Navigating Complexity: The Top Three Challenges in International Trade Compliance and Trade Compliance as a Growth Enabler: Top Three Traits of High-Performing Companies.